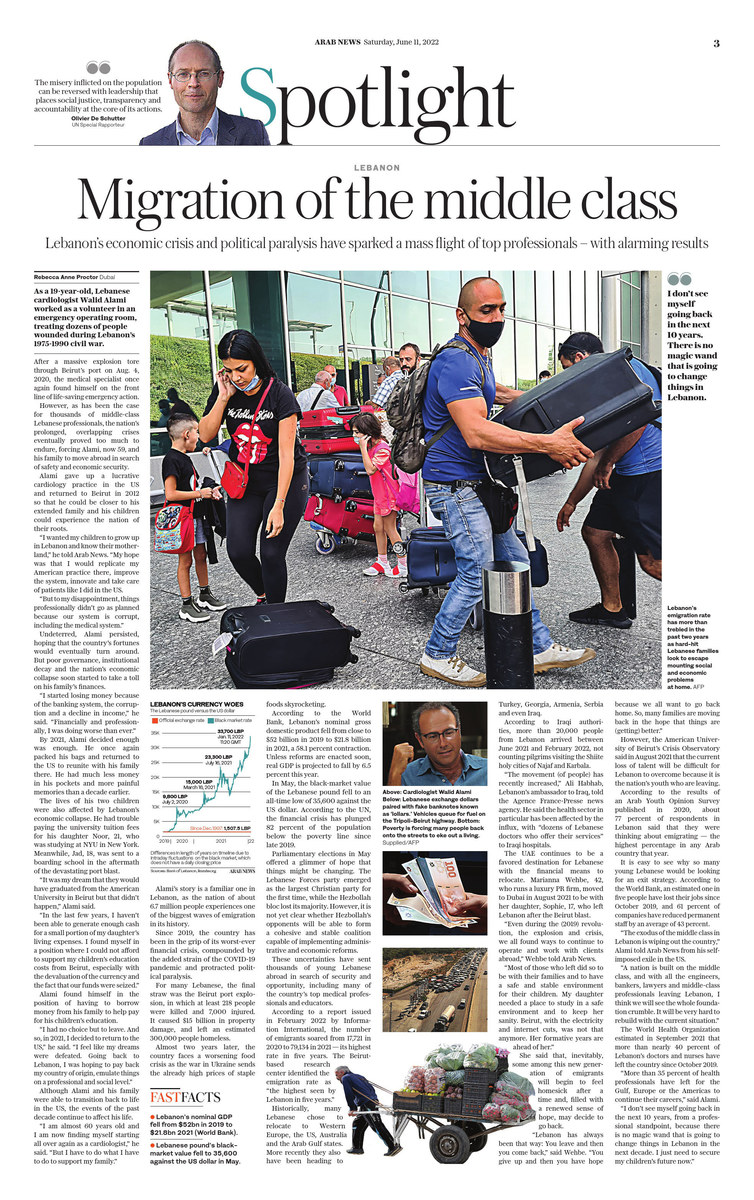
DUBAI: When Lebanese cardiologist Walid Alami, 59, was 19 years old he worked as a volunteer in an emergency operating room and helped dozens of people who were wounded during Lebanon’s 1975-1990 civil war.
After a massive explosion tore through Beirut’s port on Aug. 4, 2020, he once again found himself in the thick of life-saving emergency action.
However, as has been the case for thousands of middle-class Lebanese professionals, the nation’s prolonged, overlapping crises eventually proved too much to endure, forcing him and his family to move abroad in search of safety and economic security.
Alami gave up a lucrative cardiology practice in the US and returned to Beirut in 2012 so that he could be closer to his extended family and his children could experience the nation of their roots.

Dr. Walid Alami. (Supplied)
“I wanted my children to grow up in Lebanon and know their motherland,” he told Arab News. “My hope was that I would replicate my American practice there, improve the system, innovate and take care of patients like I did in the US.
“But to my disappointment, things professionally didn’t go as planned because our system is corrupt, including the medical system.”
Undeterred, Alami persisted, hoping that the country’s fortunes would eventually turn around. But poor governance, institutional decay and the nation’s economic collapse soon started to take a toll on his family’s finances.
“I started losing money because of the banking system, the corruption and a decline in income,” he said. “Financially and professionally, I was doing worse than ever.”
By 2021, Alami decided enough was enough. He once again packed his bags and returned to the US to reunite with his family there. He had much less money in his pockets and more painful memories than a decade earlier.
The education of his two children was also affected by Lebanon’s economic collapse. He had trouble paying the university tuition fees for his daughter Noor, 21, who was studying at NYU in New York. Meanwhile, Jad, 18, was sent to a boarding school in the aftermath of the devastating port blast.
“It was my dream that they would have graduated from the American University in Beirut but that didn’t happen,” Alami said.
“In the last few years, I haven’t been able to generate enough cash for a small portion of my daughter’s living expenses. I found myself in a position where I could not afford to support my children’s education costs from Beirut, especially with the devaluation of the currency and the fact that our funds were seized.”

A Lebanese activist displays fake banknotes called "Lollars", in front of a mock ATM, during a stunt to denounce the high-level of corruption that has wrecked the country. (AFP)
Alami found himself in the position of having to borrow money from his family to help pay for his children’s education.
“I had no choice but to leave. And so, in 2021, I decided to return to the US,” he said. “I feel like my dreams were defeated. Going back to Lebanon, I was hoping to pay back my country of origin, emulate things on a professional and social level.”
Although Alami and his family were able to transition back to life in the US, the events of the past decade continue to cast a dark shadow.
“I am almost 60 years old and I am now finding myself starting all over again as a cardiologist,” he said. “But I have to do what I have to do to support my family.”
Alami’s story is a familiar one in Lebanon, as the nation of about 6.7 million people experiences one of the biggest waves of emigration in its history.
Since 2019, the country has been in the grip of its worst-ever financial crisis, compounded by the strain of the COVID-19 pandemic and protracted political paralysis.
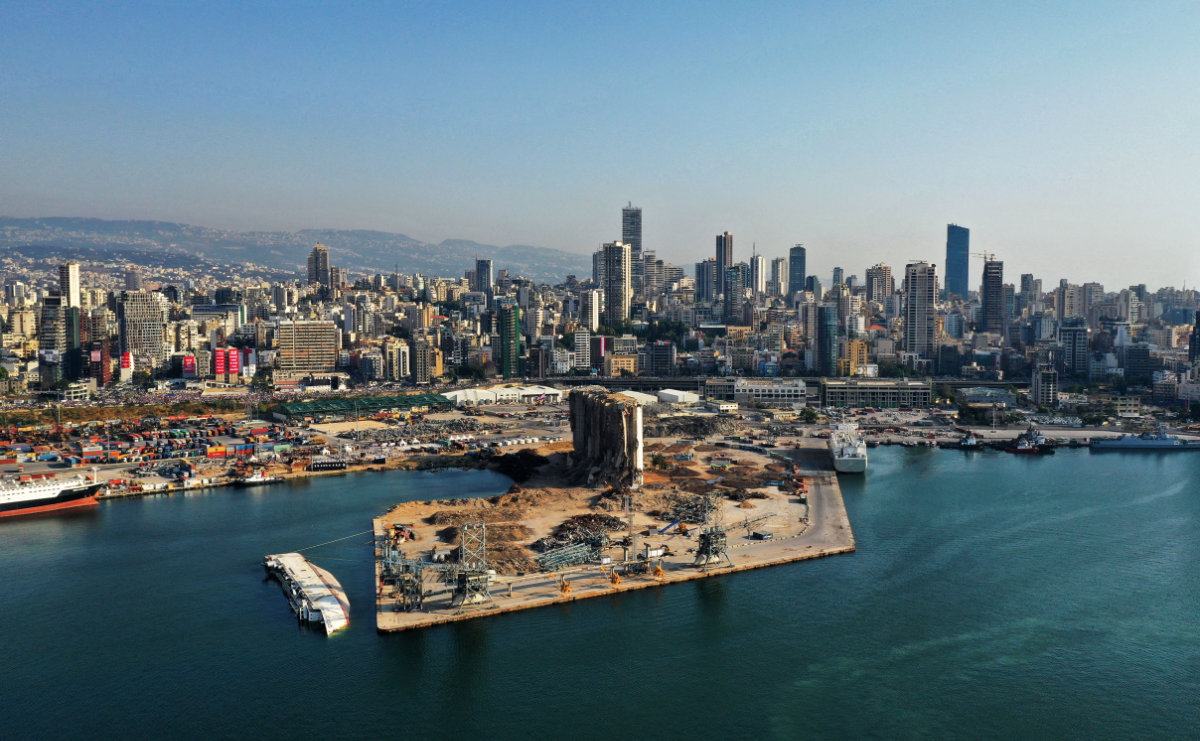

Beirut's port blast of Aug. 4, 2021, which left 218 dead and 7,000 injured, was the last straw for many Lebanese. (AFP)
For many Lebanese, the final straw was the Beirut port explosion, in which at least 218 people were killed and 7,000 injured. It caused $15 billion in property damage, and left an estimated 300,000 people homeless.
Almost two years later, the country faces a worsening food crisis as the war in Ukraine sends the already high prices of staple foods skyrocketing.
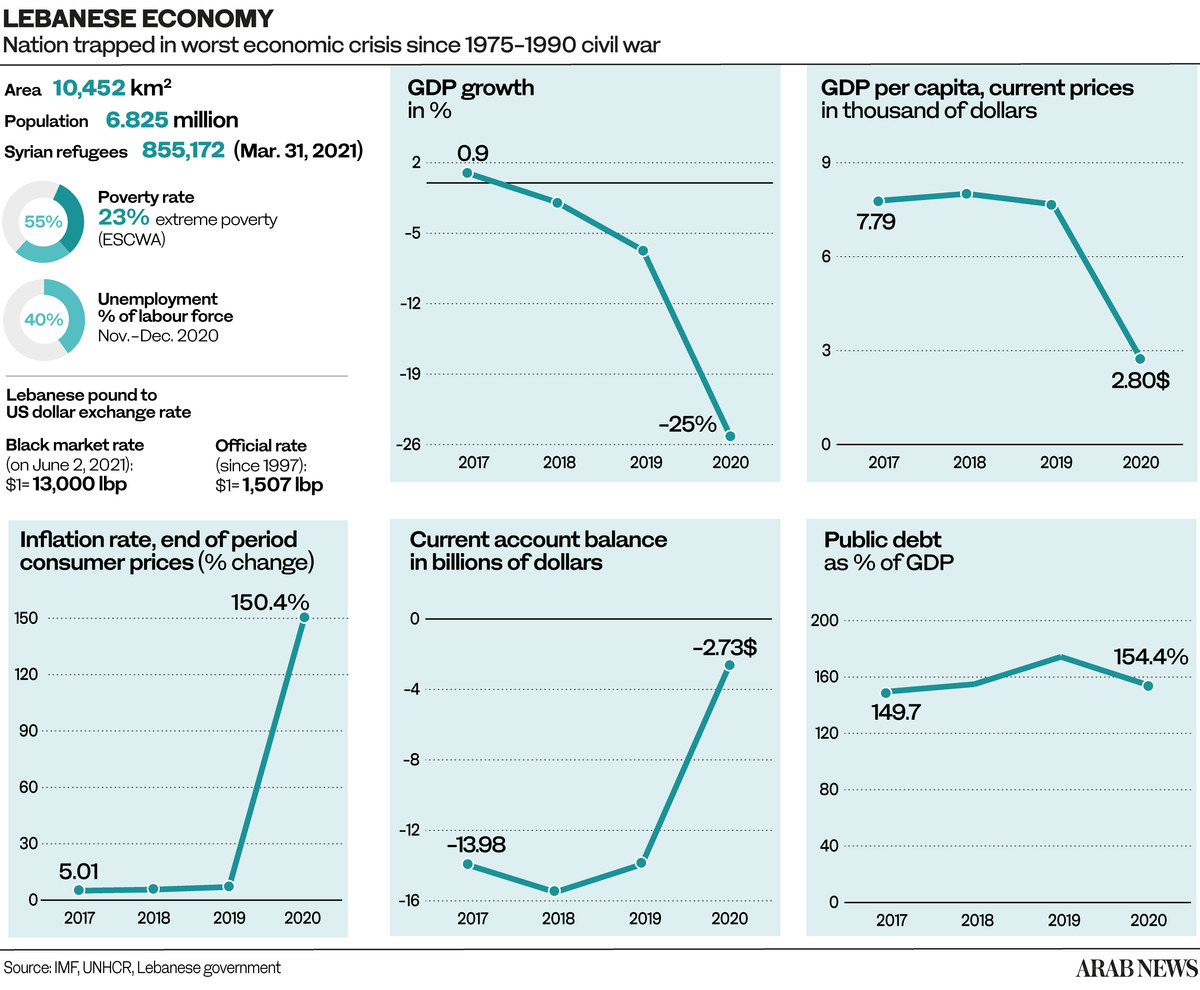
According to the World Bank, Lebanon’s nominal gross domestic product fell from close to $52 billion in 2019 to $21.8 billion in 2021, a 58.1 percent contraction. Unless reforms are enacted soon, real GDP is projected to fall by 6.5 percent this year.
In May, the black-market value of the Lebanese pound fell to an all-time low of 35,600 against the US dollar. According to the UN, the financial crisis has plunged 82 percent of the population below the poverty line since late 2019.

Parliamentary elections in May offered a glimmer of hope that things might be changing. The Lebanese Forces party emerged as the largest Christian party for the first time, while the Hezbollah bloc lost its majority. However, it is not yet clear whether Hezbollah’s opponents will be able to form a cohesive and stable coalition capable of implementing administrative and economic reforms.
These concurrent uncertainties have sent thousands of young Lebanese abroad in search of security and opportunity, including many of the country’s top medical professionals and educators.
According to a report issued in February 2022 by Information International, the number of emigrants soared from 17,721 in 2020 to 79,134 in 2021 — its highest rate in five years. The Beirut-based research center identified the emigration rate as “the highest seen by Lebanon in five years.”
A sharp increase in emigration was also recorded between mid-December 2018 and mid-December 2019, with 66,800 Lebanese emigrating, compared with 33,841 during the same period in 2018.
Historically, many Lebanese chose to relocate to Western Europe, the US, Australia and the Arab Gulf states. More recently they also have been heading to Turkey, Georgia, Armenia, Serbia and even Iraq.
According to Iraqi authorities, more than 20,000 people from Lebanon arrived between June 2021 and February 2022, not counting pilgrims visiting the Shiite holy cities of Najaf and Karbala.
FASTFACTS
Lebanon’s nominal GDP fell from $52bn in 2019 to $21.8bn 2021 (World Bank).
The Lebanese pound’s black-market value fell to 35,600 against the US dollar in May.
“The movement (of people) has recently increased,” Ali Habhab, Lebanon’s ambassador to Iraq, told the Agence France-Presse news agency. He said the health sector in particular has been affected by the influx, with “dozens of Lebanese doctors who offer their services” to Iraqi hospitals.
The UAE continues to be a favored destination for Lebanese with the financial means to relocate. Marianna Wehbe, 42, who runs a luxury PR firm, moved to Dubai in August 2021 to be with her daughter, Sophie, 17, who left Lebanon after the Beirut blast.
“Even during the (2019) revolution, the explosion and crisis, we all found ways to continue to operate and work with clients abroad,” Wehbe told Arab News.
“Most of those who left did so to be with their families and to have a safe and stable environment for their children. My daughter needed a place to study in safety and to keep her sanity. Beirut, with the electricity and internet cuts, was not that anymore. Her formative years are ahead of her.”
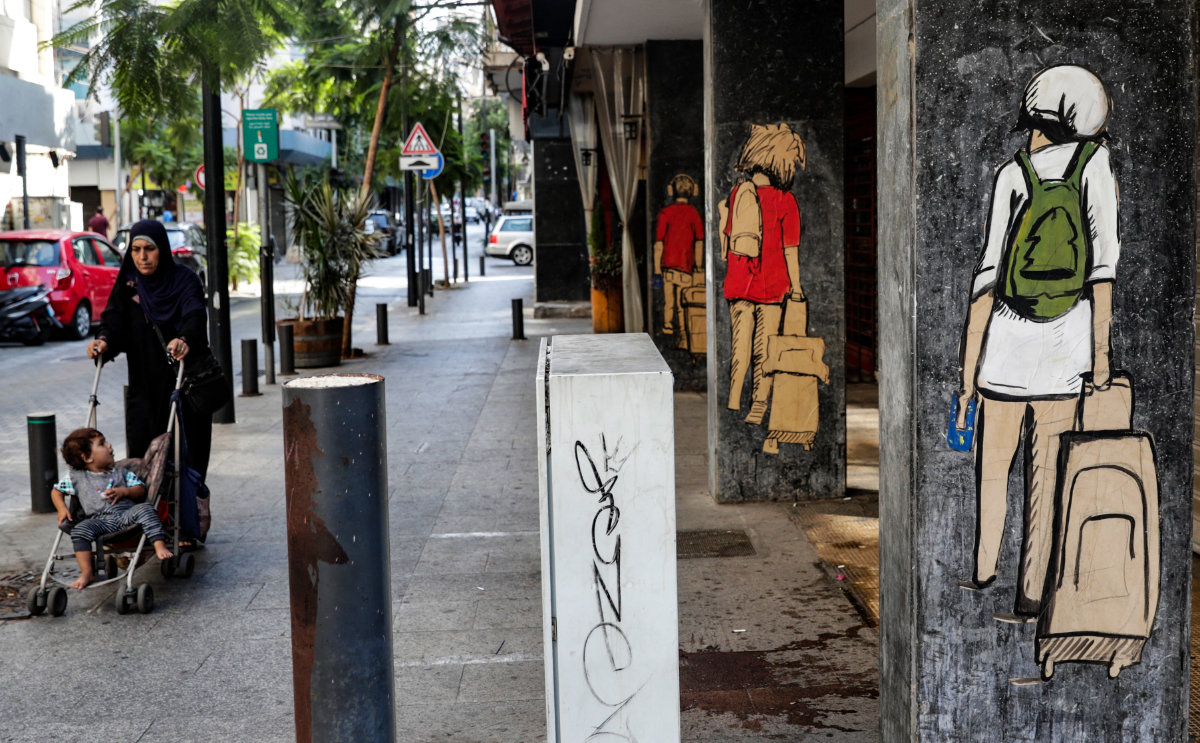

Paintings that represent migrating Lebanese youths are seen along a street in Beirut's Hamra district. (AFP file photo)
She said that, inevitably, some among this new generation of emigrants will begin to feel homesick after a time and, filled with a renewed sense of hope, may decide to go back.
“Lebanon has always been that way: You leave and then you come back,” said Wehbe. “You give up and then you have hope because we all want to go back home. So, many families are moving back in the hope that things are (getting) better.”
However, the American University of Beirut’s Crisis Observatory said in August 2021 that the current loss of talent will be difficult for Lebanon to overcome because it is the nation’s youth who are leaving.
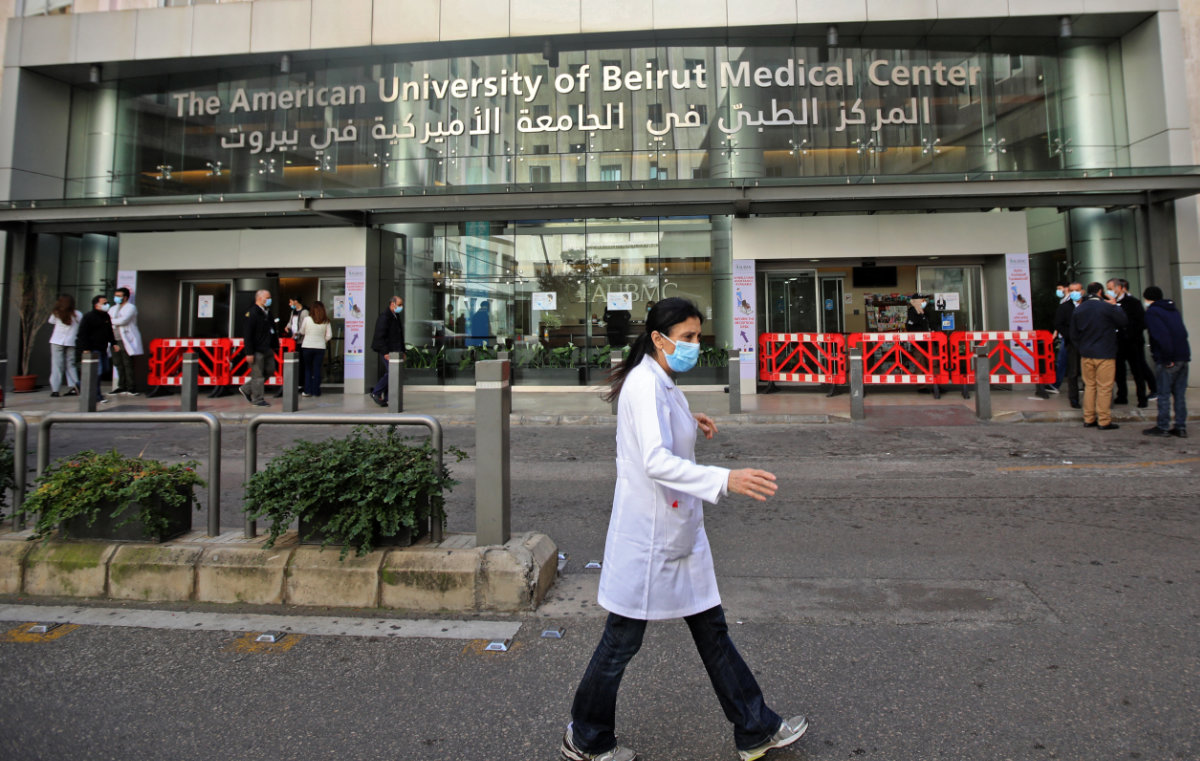

Lebanon's famous American University has lost its luster as a result of the country's unmitigated economic crisis. (AFP file photo)
According to the results of an Arab Youth Opinion Survey published in 2020, about 77 percent of respondents in Lebanon said that they were thinking about emigrating — the highest percentage in any Arab country that year.
It is easy to see why so many young Lebanese would be looking for an exit strategy. According to the World Bank, an estimated one in five people have lost their jobs since October 2019, and 61 percent of companies have reduced permanent staff by an average of 43 percent.
“The exodus of the middle class in Lebanon is wiping out the country,” Alami told Arab News from his self-imposed exile in the US.

The increasing difficulties faces by families in Lebanon has forced many to seek better life abroad. (AFP)
“A nation is built on the middle class, and with all the engineers, bankers, lawyers and middle-class professionals leaving Lebanon, I think we will see the whole foundation crumble. It will be very hard to rebuild with the current situation.”
The World Health Organization estimated in September 2021 that more than nearly 40 percent of Lebanon’s doctors and nurses have left the country since October 2019.
“More than 35 percent of health professionals have left for the Gulf, Europe or the Americas to continue their careers,” said Alami.
“I don’t see myself going back in the next 10 years, from a professional standpoint, because there is no magic wand that is going to change things in Lebanon in the next decade. I just need to secure my children’s future now.”